Contact us
Please leave your specific needs and contact information, and the staff will contact you as soon as possible!
A cone crusher is a type of equipment used in mining and aggregate industries to crush a variety of materials, such as hard and medium-hard rocks, ores, and minerals. It is commonly used in the secondary, tertiary, and quaternary crushing stages. The crushing process is achieved by compressing the material between a mantle (concave surface) and a bowl-shaped bearing (concave). To make this possible, a cone crusher consists of several parts, each serving a specific function.
Those cone crusher parts include:
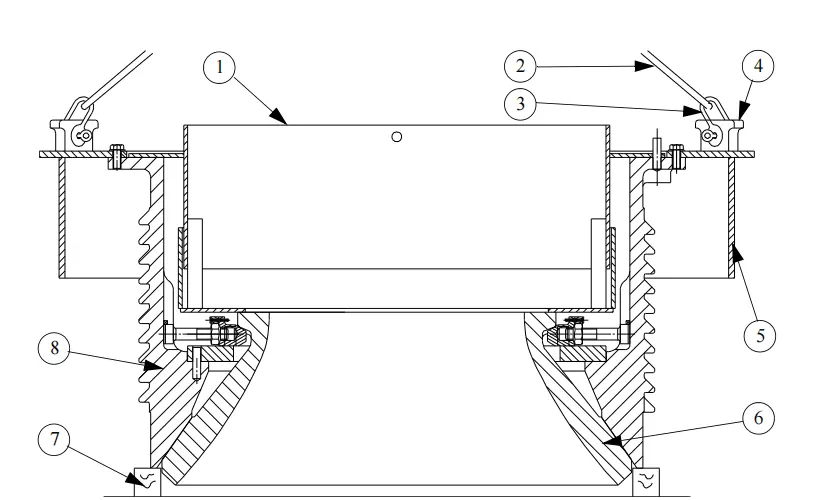
The bowl is screwed inside the adjusting ring, adjustments are made by rotating the bowl anticlockwise or clockwise, according to the desired setting.
Bowl adjustment determines the gap between the bowl liner and mantle.
The adjustment cap is fixed on top of the bowl and rubs against the joint of the protective apron that is fixed to the adjusting ring. This is done to protect the bowl and the locking ring. A set of locking cylinders are present at the top of the adjusting ring and around it. These cylinders push the locking ring and raise the bowl to the crushing position. The bowl rotates with the adjustment cap with the help of a hydraulic motor that is mounted on the adjusting ring.
The hopper is placed on two pins on the upper edge of the bowl. The inside of the hopper feeds the crusher cavity directly. The shape of the bottom of the hopper is designed in such a way that the materials build up there, forming a dead-bed that protects the hopper against the flow of feed material.
Several wedges and screws are present under the hopper and on the bowl, which hold the liner firmly on the bowl.
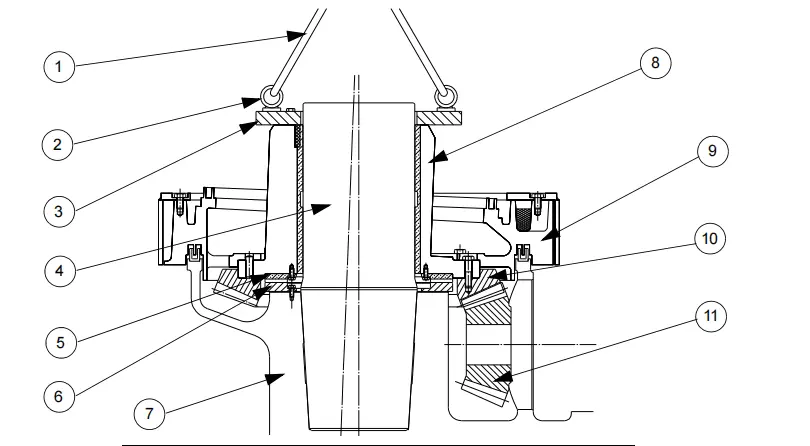
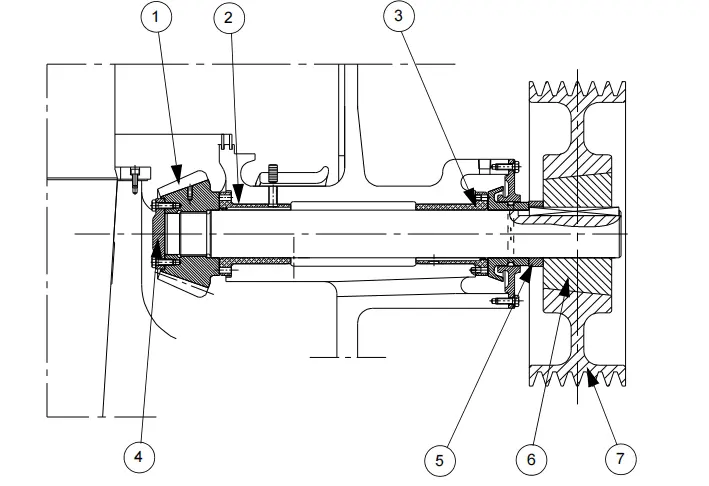
The crusher cavity is formed by the head, mantle, bowl, and bowl liner. The mantle is firmly held against the head with the help of a locking nut. The feeder cone rotates with the head and distributes materials in the crusher cavity.
The head has a bore that receives the head ball. The head ball is mounted tightly into the head. Two bores receive a bushing (upper and lower) that is also tightly mounted. The head ball rests on the concave part of the spherical bearing at the top of the main shaft. The lower head bushing is mounted with the play on the eccentric, and the head’s rotation is driven by being in contact with the ring and the eccentric.
When the machine is running idle, the upper head bushing comes into contact with the sleeve to maintain contact between the head ball and the sleeve. Holes in the main shaft guide the oil towards the upper and lower head bushings and into the spherical bearing.
A U-shaped seal machined over the imbalance matches the T-shaped seal mounted in a groove under the head to prevent oil leaks and protect the crown, pinion, and bushing surfaces from dust. A skirt acting as an oil deflector prevents leaks through the labyrinth seal.
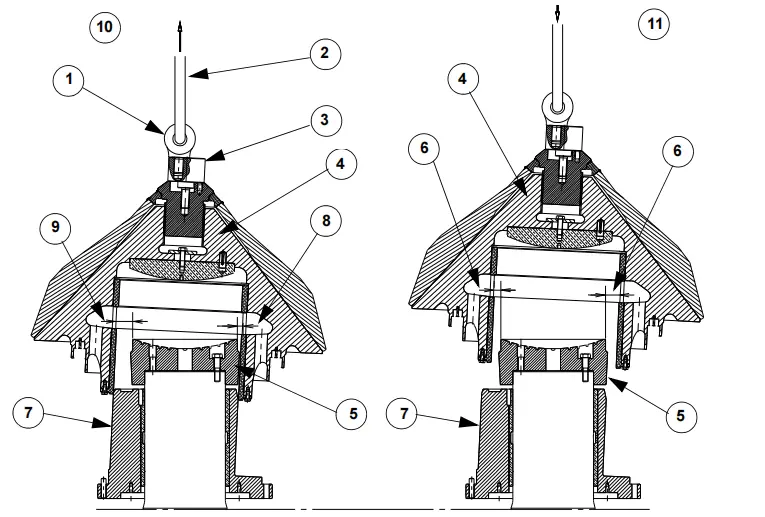
The head assembly is supported by a sleeve that has a spherical bearing. This sleeve helps in transmitting the crushing force to the frame and is mounted on the shaft. It is fixed with screws.
The head ball is bolted under the head and is protected by the spherical bearing that is pinned to the top of the sleeve. The upper surface of the bearing is made up of circular oil grooves. The bearing is lubricated by pressurized oil flowing through the passages between the main shaft and the sleeve.
The eccentric part of the machine is positioned slightly off-center and at an angle to the vertical axis of rotation. This transmits the movement to the head. Inside the eccentric, there is a bronze ring, and at the bottom, a toothed crown is bolted to the eccentric.
The crown is driven by the countershaft pinion. The whole eccentric assembly rotates around the main shaft. The assembly rests on thrust bearings, with the upper thrust washer made of bronze and fixed to the bottom of the eccentric. The lower thrust washer is made of steel and fixed to the frame. These washers help to prevent wear in the assembly due to friction.
Adjusting wedges are used to maintain the play between and at the bottom of the teeth between the crown and the pinion. The imbalance is asymmetrical, so the greatest weight is positioned directly opposite the centrifugal force generated by the swaying of the head.
This imbalance creates an oil and dust seal between the rotating head and the fixed main frame. A system of baffles with “U” and “T” joints is used to maintain the seal.
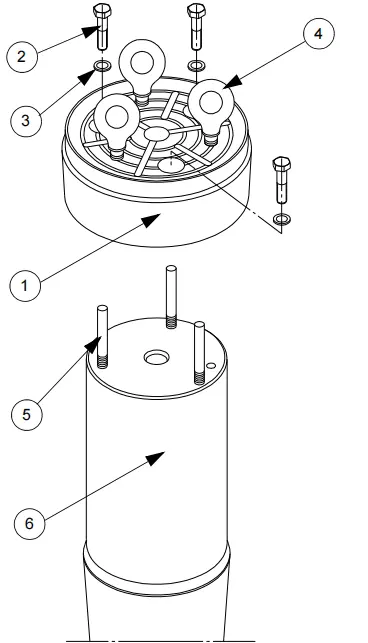
The crusher’s countershaft motor receives power through either a V-belt transmission or a coupling sleeve, with a pinion at one end of the countershaft transmitting its rotation to the eccentric using a toothed crown.
The countershaft is supported by two bronze bushings, which are fixed in place by pins in the countershaft housing. These bushings have a flange that receives the axial load from the pinion and the oil deflector. The oil deflector is tightly inserted on the control side of the countershaft to spin the oil from the bushings’ lubrication and deposit it onto the cover.
The countershaft housing returns the oil to the tank, and it is firmly attached with large screws. An O-ring seal or a lip seal creates the oil seal between the frame and the countershaft housing, and a shield protects the countershaft housing from wear caused by falling crushed materials.
The frame, whether bolted to its foundations or mounted on a metal chassis with vibration dampers, provides an unyielding backbone for various components. The inside of the frame is safeguarded against wear by a liner that is welded to it, and arm liners that require periodic replacement.
The adjusting ring, which has a female thread for controlling the bowl, sits on a conical seating that is machined in the upper part of the frame. To prevent the bowl from turning during crushing, cylinders placed between the locking ring and the adjusting ring are used to press the locking ring against the inner face of the bowl threads. An apron fixed to the adjusting ring shields the locking cylinders and the bowl’s threads from dust.
Hydraulic cylinders pinned to the frame and traversing the adjusting ring keep the ring firmly pressed against the conical part of the frame. Under abnormal operating conditions or when tramp iron is detected in the crusher, the cylinder’s rods may pull and lift the bowl and the adjusting ring, causing strain. This movement forces the oil in the cylinders into the accumulators, where the nitrogen pressure increases.
Once the excess load has been released, the compressed nitrogen returns the oil to the cylinders, and the cylinder rods retract, causing the adjusting ring to return to its resting position on the frame. When the adjusting ring lifts off the frame, it is guided by vertical pins fixed to the frame.
Finally, the eccentric is supported by a thrust washer that is bolted to the frame’s drum, and play between and at the bottom of the teeth of the crown, and pinion is adjusted by wedges inserted under the washer.
Qiming Casting produces wear parts for cone crushers that are highly wear-resistant, easy to install, and have a longer lifespan. They achieve this by working closely with cone crusher users to understand their needs.
In addition to standard manganese liners (Mn14, Mn18, Mn22), Qiming Machinery also provides wear parts made from a variety of materials to meet the diverse needs of their customers.
Learn more about Qiming Casting cone crusher liner solutions→
Qiming Casting is the leading provider of high-quality aftermarket spare parts based on original drawings. We have successfully supplied replacement adjustment rings, eccentric bushing, head balls, countershafts, sleeves, and other spare parts for cone crushers and other major components that are no longer produced by the original equipment manufacturer.
Furthermore, we offer unbeatable OEM/ODM services for cone crusher parts that can be customized to meet your personalized requirements, including brand, label, painting colors, and packing box.
With our cutting-edge technology and experienced R&D team, we are confident in our ability to exceed your expectations. Don’t settle for less, choose Qiming Casting for all your spare parts needs.
Some common problems and solutions for cone crusher parts during machine operation